Sir Alex Ferguson was always going to be a tough act to follow at Manchester United and so it proved as David Moyes’ brief reign ended with him being sacked after a poor season and the club failing to qualify for European competition for the first time since 1990.
He was in turn replaced by Louis van Gaal, whose side also struggled at times, but the Dutchman has a great track record, not to mention a larger-than-life personality, and did ultimately lead United back into Europe by finishing fourth in the Premier League in 2014/15.
So what difference has the absence of the Champions League made to United’s financial results?
The answer is “quite a lot”, as the bottom line was some £45 million worse than the previous season, with the club moving from a £40.5 million pre-tax profit in 2013/14 to a £4.0 million loss in 2014/15 – though clearly there are other factors that have also influenced these numbers.
The reduction in profitability after tax was not quite so large, as there was a tax credit of £2.8 million compared to an expense of £16.7 million the prior year, meaning that the profit after tax of £23.8 million fell £25.0 million to a loss of £1.2 million.
Revenue dropped £38 million (9%) from £433 million to £395 million, largely due to decreases in broadcasting revenue of £28 million and match day revenue of £18 million, which reflected the lack of Champions League participation. This was partly offset by an £8 million increase in commercial income, mainly from the new General Motors shirt sponsorship deal.
The revenue fall was compensated by lower costs, also largely linked to no European qualification: (a) the wage bill was cut by £12 million (6%) to £203 million, as there were no Champions League bonus payments; (b) other expenses decreased by £16 million (18%) to £73 million, partly due to lower costs of hosting fewer European home games.
"Twist and Shout"
On the other hand, player amortisation was £44 million (80%) higher at almost £100 million, reflecting the significant spend on bringing in new players, though player trading was helped by profits on player sales being £17 million higher at £24 million. Net financing costs rose £8 million to £35 million, mainly due to paying a premium for yet another debt refinancing.
Finally, exceptional items were £3 million lower, as last season the club had to absorb a £5 million compensation payment to Moyes and his coaching team, while the 2014/15 figures included £2 million professional fees relating to a shares sale.
All in all, these results were pretty “solid”, to use vice-chairman Ed Woodward’s adjective, and demonstrated United’s ability to withstand “short-term headwinds”, i.e. missing out on the Champions League.
In 2013/14, which was a more “normal” season for United, they had the second highest profits in the Premier League of £41 million, only surpassed by Tottenham Hotspur’s £80 million, but ahead of Southampton £29 million and Everton £28 million. Although football clubs have traditionally struggled to make money, the new TV deals have driven most clubs in the top flight towards profitability with only five reporting a loss that season (the most recent year when all clubs have published their annual accounts).
Then again, profits on player sales can also be very important to these figures. While United only made £7 million from disposals in 2013/14, including the low-key sales of Alex Büttner to Dynamo Moscow and Scott Wootton to Leeds United, other clubs generated sizeable profits from this activity: Tottenham £104 million (largely Gareth Bale to Real Madrid), Chelsea £65 million (David Luiz to PSG), Southampton £32 million (Adam Lallana to Liverpool) and Everton £28 million (Marouane Fellaini to Manchester United).
In other words, United were the only one of the top four clubs in the profit league to reach this position without the benefit of high value player sales, which is a testament to their underlying business model.
However, as we have seen, United’s 2014/15 accounts included much higher profits on player sales of £24 million, mainly from the transfer of Danny Welbeck to Arsenal, but also including the returns of Shinji Kagawa to Borussia Dortmund and Wilfried Zaha to Crystal Palace plus Michael Keane to Burnley and Bebé to Benfica. This is the highest amount United have generated from transfers since 2009.
This is the third time in the last four years that United have made a small pre-tax loss: £5 million in 2012, £9 million in 2013 and £4 million in 2015. The largest loss recently was the £44 million reported in 2010, which was largely caused by £109 million of financing costs. This was actually lower than the £117 million of financing costs the previous season, but was compensated by the £80 million profit on player sales, almost entirely from Cristiano Ronaldo’s move to Real Madrid.
Of course, United’s profits would have been substantially higher if the club did not have to bear the financing costs of the Glazers’ leveraged buy-out. In fact, over the last seven years they have made total operating profits of £457 million (including £148 million from player sales), which have been totally wiped out by net financing costs of £460 million.
The other side of player trading is obviously player purchases, where the recent huge increase in spending has been reflected in United’s profit and loss account via player amortisation, which shot up from £55 million to £100 million in 2014/15. In fact, this expense has increased by a whopping £62 million from £38 million four years ago. For the same reason, player asset values on the balance sheet have risen to £238 million.
Unsurprisingly, United's player amortisation is now the largest in the Premier League, though Manchester City are likely to be close to this amount when they publish their 2014/15 accounts. Basically, those clubs that are regarded as big spenders logically have the highest amortisation charges, e.g. Manchester City £76 million and Chelsea £72 million in 2013/14, while Arsenal’s relatively restrained spending has left them with £54 million of player amortisation in 2014/15.
Although this is fairly technical, it is important to understand that transfer fees are not fully expensed in the year a player is purchased, but the cost is spread evenly over the length of the player’s contract – even if the entire fee is paid upfront. As an example, Morgan Schneiderlin was reportedly bought for £24 million on a four-year deal, so the annual amortisation in the accounts for him is £6 million.
The fundamental point is that when a club purchases a player the costs are spread over a few years, but any profit made from selling players is immediately booked to the accounts, which helps explain why clubs like Manchester City can spend so much and still meet UEFA’s Financial Fair Play targets.
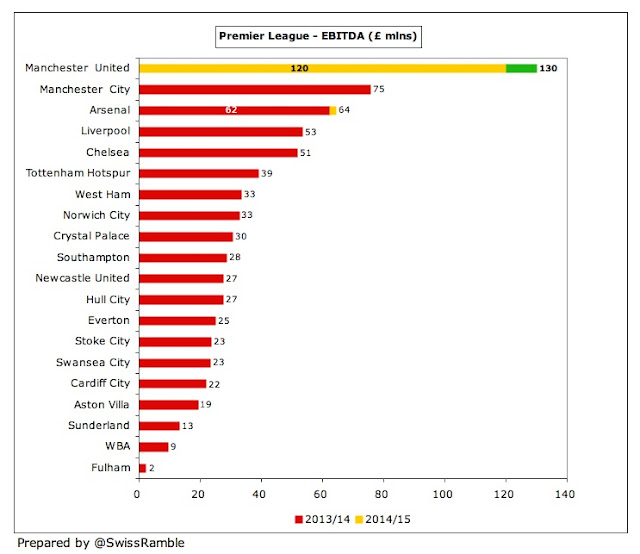
As a result of these accounting shenanigans, clubs often look at EBITDA (Earnings Before Interest, Depreciation and Amortisation) for a better idea of underlying profitability. On this basis, United are the undisputed champions, as their operations have produced enormous cash flow over the years.
Despite a fall in 2014/15 from £130 million to £120 million, this is still substantially more than other clubs, e.g. Arsenal’s EBITDA of £64 million is only around half of United’s, while Manchester City’s 2013/14 figure was also much lower at £75 million. Indeed, United are projecting an astonishing £165-175 million of EBITDA for 2015/16.
Revenue decreased by 9% (£38 million) from the record £433 million in 2013/14 to £395 million last season, with steep declines in both broadcasting 21% (£28 million) to £108 million and match day 16% (£18 million) to £91 million, partially offset by a 4% (£8 million) increase in commercial income.
Even though commercial income grew overall, it is worth noting that it is not all good news here, as this was only due to sponsorships rising £19 million to £155 million, while both other commercial revenue streams fell: retail, merchandising and product licensing by £6 million to £32 million, primarily due to reduced Nike revenue from non-participation in UEFA competitions; and mobile and content revenue by £6 million to £10 million, due to the expiration of a few mobile partnerships.
In fact, this is the second year in a row that United have earned less revenue from these commercial activities, which has been somewhat obscured by the headline growth in sponsorships.
United’s revenue of £433 million was a long way above the other Premier League clubs in 2013/14 with the closest challengers being Manchester City £347 million, Chelsea £320 million and Arsenal £299 million. Despite Arsenal’s revenue rising to £329 million, United are still £66 million ahead, even after their fall to £395 million.
It is possible that City will overtake their neighbours in 2014/15, though this is only likely to be a temporary “victory”, as United are estimating revenue of £500-510 million in 2015/16 following their return to the Champions League and the record Adidas kit deal, which would make them the first English club to break through the half-billion pounds barrier.
This is important, as budget is closely correlated with success in the pitch. United climbed to second place in the Deloitte 2014 Money League, only behind Real Madrid with £460 million, but ahead of Bayern Munich and Barcelona. In contrast to United, both Spanish giants have announced good revenue growth in 2014/15: Real Madrid up 5% to €578 million, Barcelona up 16% to €561 million – though their revenue in Sterling terms will be impacted by the weakness of the Euro.
It is genuinely possible that United will actually top the Money League in 2015/16, given their projected revenue, though this will obviously depend on how the other elite clubs perform and how the Euro exchange rate develops.
If we compare the revenue of the other nine clubs in the Money League top ten, we can see how strongly United performed in 2014. They were ahead of all other clubs in terms of match day income, while they only suffered compared to Real Madrid and Barcelona in broadcasting revenue, thanks to the Spanish clubs’ individual TV deals.
Commercially, they were only substantially outperformed by Paris Saint-German, whose £274 million massively benefited from the French club’s “friendly” agreement with the Qatar Tourist Authority, and Bayern Munich, whose £244 million emphasised their commercial dominance in Germany.
Nevertheless, United’s commercial revenue is still the envy of almost every other club, which is highlighted by this stream accounting for 50% of their total revenue, up from 44% in 2013/14. Broadcasting is lower at 27%, as is match day at 23%, yet again reflecting the absence from the Champions League.
Domestically, United are still the brightest star in commercial terms. Their 2014/15 revenue of £196 million is nearly twice as much as Arsenal, even after the London club’s 34% growth last season. In 2013/14 United increased the gap to their nearest challengers, Manchester City, who were £23 million lower at £166 million, though it will be interesting to see City’s 2014/15 numbers.
Both Manchester clubs are miles ahead of the other English clubs with the next highest being Chelsea £109 million, Liverpool £104 million and Arsenal £103 million. And remember, this is all before United’s blockbuster new deal with Adidas commences in 2015/16.
United described this as the “largest kit manufacture sponsorship deal in sport”, as it is worth £750 million over 10 years – or an average of £75 million a year. This is, deep breath, £50 million higher than the current Nike deal.
It is true that success clauses are built into this contract, e.g. if United fail to participate in the Champions League for two or more consecutive seasons starting with the 2015/16 season, then the payment for that year would reduce up to 30%, but it is still an astonishing deal, significantly higher than the £30 million agreements at Arsenal (PUMA) and Chelsea (Adidas).
In addition, retail, e-commerce and licensing will revert to United from August 2015, as opposed to the current deal whereby any profits generated from these activities is shared equally between the club and Nike.
United’s ability to “successfully monitise our brand” and extract value from their sponsorship deals is almost unprecedented. General Motors (Chevrolet) signed a seven-year deal running to the end of the 2020/21 season worth $70 million (£46 million) in the first season, rising by an additional 2.1% each season afterwards. Amazingly, GM also paid United $18.6 million in each of the 2012/13 and 2013/14 seasons for “pre-sponsorship support and exposure”. The next highest shirt sponsorship deals are Chelsea (Yokohama) £40 million and Arsenal (Emirates) £30 million.
United’s previous shirt sponsors, Aon, have not completely exited the scene though, as they will pay for the privilege of being United’s training kit partner until 2020/21 including renaming the training facilities at Carrington as the Aon Training Complex.
"A Bastian of respectability"
On top of that, United continue to announce new sponsorships. In 2014/15 alone this included 5 global sponsors, 4 regional sponsors and 2 financial services and telecom partnerships.
United also earn good money from promotional tours and exhibition matches, e.g. £11 million in 2013/14. However, the Glazers have drawn the line at selling naming rights to the Old Trafford stadium, which are potentially worth £20 million a year.
United’s share of the Premier League television money was £97 million in 2014/15, up £8 million from £89 million the previous season, primarily due to increases in the merit payment and facility fees due to finishing three places higher in the league and having two more games broadcast live.
This is even before the increases from the mega Premier League TV deal in 2016/17. My estimates suggest that United’s fourth place would be worth an additional £49 million under the new contract, increasing the total received to £146 million. This is based on the contracted 70% increase in the domestic deal and an assumed 30% increase in the overseas deals (though this might be conservative, given some of the deals announced to date).
The other main element of broadcasting revenue is European competition, but obviously United got no money here in 2014/15, as opposed to the €45 million they received the previous season for reaching the Champions League quarter-final (which is in line with the club’s budget assumption).
The value of Champions League qualification is clear, especially if it is compared to the Europa League, where the most earned by an English club in 2013/14 was Tottenham’s €6 million, so it was obviously vital that van Gaal’s team came through their qualifying tie with Club Brugge last month.
The financial significance of a top four placing is even more pronounced from the 2015/16 season with the new Champions League TV deal worth an additional 40-50% for participation bonuses and prize money and further significant growth in the TV (market) pool thanks to BT Sports paying more than Sky/ITV for live games.
United’s 2015/16 Champions League payment will partly depend on how far they progress in the tournament, but is to an extent compromised by their 4th place finish in the 2014/15 Premier League. This is because half of the market pool is allocated based on the finishing place in the previous season’s domestic league: 1st place 40%, 2nd place 30%, 3rd place 20% and 4th place 10%. The revenue will also be adversely affected in Sterling terms by the weaker Euro.
United’s match day revenue fell 16% (£18 million) from £108 million to £91 million in 2014/15, falling behind Arsenal’s £100 million, but still a long way ahead of other English clubs, e.g. Chelsea £71 million, Liverpool £51 million and Manchester City £47 million. The decrease is due to having seven fewer home games, largely because of the non-participation in Europe.
United’s average attendance of 75,000 is far higher than any other English club (Arsenal being the nearest at just under 60,000), which allows them to have tickets that are “fairly priced compared to the market” in Woodward’s words. Season ticket prices were frozen for the 2015/16 season, representing the fourth consecutive season, and the fifth time in six years, that prices have been held.
However, the club places great emphasis on its premium seating and hospitality facilities in order to maximise match day revenue, as can be seen by Old Trafford (“the theatre of dreams”) having 154 luxury boxes, approximately 8,000 executive club seats, 15 restaurants and 4 sports bars. In fact, the 2014 revenue included £54 million from gate receipts and £33 million from hospitality.
United’s wage bill decreased by 6% (£12 million) from £215 million to £203 million, primarily as a consequence of no bonuses being paid for Champions League qualification, though the wages to turnover ratio rose slightly from 50% to 51% following the fall in revenue.
This is higher than the 44-46% achieved between 2009 and 2011, but is basically in line with the ratio of the last three seasons and is in fact one of the lowest (i.e. best) in the Premier League.
United’s wage bill was the highest in the Premier League in 2013/14, having overtaken Manchester City, but the fall to £203 million puts the Red Devils lower than City once again and just £10-11 million more than Chelsea and Arsenal.
Of course, United fans will be quick to point out that City’s 2014/15 wage bill might well have gone up and will also have noted that some of City’s decrease is due to a group restructure whereby some staff are now paid by group companies with the costs included in external charges, as opposed to wages.
One point that was not fully explained in United’s press release was the significant reduction in the number of employees of 101 from 879 to 778.
In any case, United’s wages are way ahead of most Premier League clubs with some of the nearest challengers (in 2013/14) being Liverpool £144 million, Tottenham £100 million and Newcastle £78 million.
The club also expects United’s wage bill to increase in 2015/16 with the return to the Champions League and the arrival of big money signings, though this will have been offset to an extent by the sales of those on sizeable wages, such as Radamel Falcao, Angel Di Maria, Robin van Persie and Nani.
Although there is a natural focus on wages, other expenses also account for a considerable part of the budget at leading clubs, though United’s decreased in 2014/15 by £16 million (18%) from £88 million to £72 million, which is exactly the same as Arsenal. The primary reason for the reduction was the lower cost of staging home games in Europe, but also due to non-recurring cost savings and foreign exchange gains.
United have really ramped up their spend in the transfer market in the last few seasons, splashing out huge sums to make up for the years of austerity (relatively speaking). In essence, Ferguson’s genius at working on a tight transfer budget delivered great results, but also resulted in a squad that needed to be substantially upgraded by his successors.
In the five years between 2006 and 2011, United’s net spend was only £13 million, a paltry sum for a club of this magnitude, though this was obviously deflated by Ronaldo’s £80 million sale to Real Madrid. However, in the following five years, the net spend has accelerated to £301 million, almost entirely due to much higher gross spend.
This included £145 million in the last two seasons, as van Gaal has recruited (expensive) new blood, including Angel Di Maria, Ander Herrera, Luke Shaw, Marcos Rojo, Daley Blind, Memphis Depay, Morgan Schneiderlin, Bastian Schneiderlin, Matteo Darmian and Anthony Martial. In fact, their net spend in this period is only surpassed by Manchester City’s £151 million, but is almost twice as high as Arsenal £74 million.
Perhaps the most eye-opening signing was Martial with United paying an initial £36 million (€50 million) for the 19-year old forward plus a potential £22 million (€30 million) add-ons. According to respected French journalist Julian Laurens, there are three bonus payments of €10 million dependent on the following achievements: 25 goals (over four seasons), 25 French caps and winning the Ballon d’Or.
Woodward has cautioned that the club may reduce its spending in future: “We have seen a large number of ins and outs in the last two summer windows. We were used to more modest numbers. Maybe we will go back to more normalized numbers.” However, as we have seen, United will generate enough cash in future for a similar outlay – if they want.
United’s gross debt rose by £69 million from £342 million to £411 million, partly due to the latest refinancing in June 2015 increasing the debt, exacerbated by the strengthening US Dollar. However, net debt fell by £20 million from £275 million to £255 million following the £90 million increase in cash balances from £66 million to £156 million.
In that refinancing, $269 million of Senior Secured Notes were redeemed with $425 million of new SSNs being issued. This slipped the repayment date from 2017 to 2027 and lowered the interest rate from 8.375% to 3.79%. At the same time, the Secured Term Facility was reduced from $316 million to $225 million. Again, the repayment date was extended from 2019 to 2025 with the interest rate cut from 1.5-2.75% to 1.25-1.75%.
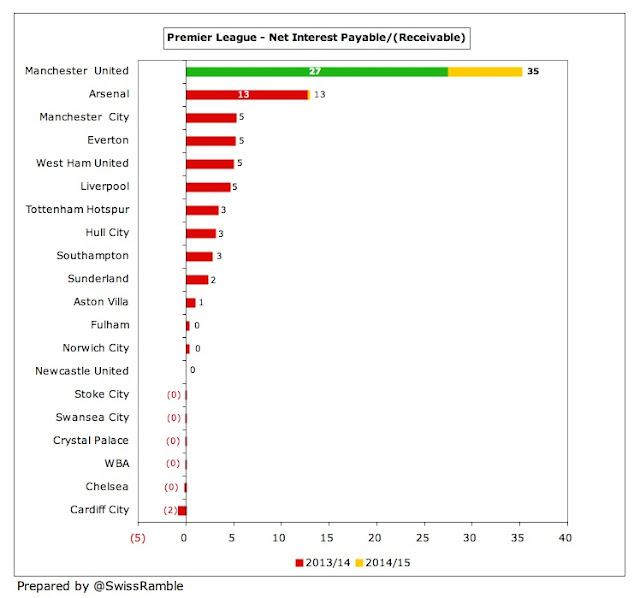
In short, the debt was increased from $585 million to $650 million, but the repayment dates were extended with a lower interest rate. According to finance director Hemen Tseayo, the annual interest payment should drop by $10 million to $20 million in future as a result of this refinancing, but there was a price to pay, as United’s net finance costs actually increased in 2014/15 from £27 million to £35 million, primarily due to the premium paid for this refinancing.
The net financing costs of £35 million is a lot more than any other Premier League club with Arsenal being the only other club with a double-digit payment of £13 million. To place that into perspective, Manchester City, Everton, West Ham and Liverpool all had net interest payable of around £5 million.
Although these interest payments are clearly manageable, United supporters would surely prefer this money to be spent on further strengthening the squad. Former chief executive David Gill famously said that “debt is the road to ruin” before the Glazers purchased the club, which has not exactly proved to be the case for United, but it has undoubtedly been damaging to their prospects.
The only other Premier League club with comparable levels of borrowing is Arsenal, whose £234 million represents the debt incurred for the construction of the Emirates Stadium. There are just four other clubs with debt above £100 million in the Premier League in 2013/14, namely Cardiff City £135 million, Newcastle United £129 million, Liverpool £127 million and Aston Villa £104 million.
United’s business model only works because of their extraordinary ability to throw off cash, as evidenced by the movements in 2014/15, when they generated £195 million of cash from operating activities (including £77 million of working capital movements, largely a reduction in receivables). They then spent a net £97 million on player registrations (£117 million of purchases less £20 million of sales), but also £49 million on interest payments (including debt finance costs related to borrowings).
There was also £5 million of infrastructure investment and £2 million of tax. Even so, cash rose £42 million before being boosted by £45 million from the latest refinancing to give a net increase of £86 million (before FX gains of £3 million).
In the last six years United have generated over £1 billion of cash: £736 million from operating activities plus £318 million from share issues. Just over £300 million (29%) of this has been spent on player purchases and £63 million (6%) on capital expenditure, but the vast majority £658 million (62%) has been used to finance the Glazers’ loans: £412 million of interest payments and £246 million of debt repayments.
As if that were not bad enough, the club announced that it will pay a £15 million dividend every year to Malcolm Glazer’s six children in the future. This was not exactly unexpected, with a similar £10 million dividend having already been paid in 2012, but it still leaves a nasty taste in the mouth, especially as the decision was made by a board that includes the very same Glazer offspring.
There is certainly enough cash available in the club’s coffers with United’s £156 million only surpassed by Arsenal’s unprecedented £228 million, but miles above all other Premier League clubs, e.g. the next highest balance in 2013/14 was Tottenham Hotspur with £39 million. That said, there are likely to still be high amounts due for transfer fees – this was not specified in the club’s press release, but was £82 million in 2014.
The Glazer family has already made $400 million from selling shares on the New York Stock Exchange, while seeing the value of their asset more than double, but announced that it is trying to raise another $400 million by selling 24 million new Class A shares.
All this at the same time as they have cost the club around £850 million in interest payments, debt repayments and professional fees. Although the exact figure is open to debate, there is no doubt that United have wasted enormous sums on the dubious pleasure of having the Glazers as owners, while those funds could have been spent on the football club in order to help the team compete on an equal basis with the very best teams in Europe.
"Give youth a chance"
In fairness, if the club had remained a PLC, then it would have had to pay out dividends and the current structure also produces tax savings, as interest expenses are tax deductible, but the net impact of the Glazers’ ownership is still hugely negative. Perhaps the worst thing is that even after all that money has disappeared into the financial ether, United’s debt mountain is still north of £400 million.
There is no doubt that United’s commercial business has thrived under the Glazers’ guidance, but surely other owners with the slightest business acumen would have done much the same with a football club that the Glazers described as “the strongest brand name in the sports world.”
"Wax and Wayne"
As the Manchester United Supporters' Trust said, “If it were a race, then United are dragging their owners behind them like a tractor, while Manchester City's owners are providing rocket fuel.”
United have been one of the biggest beneficiaries of UEFA’s Financial Fair Play (FFP) regulations, thanks to their massive revenue. Some are under the impression that FFP has disappeared, but this is not the case. Ed Woodward confirmed that the basic rules remain in place, though the subtle difference is that new owners will now be allowed to make larger losses, as long as they can produce a business plan that will show how they will reach break-even.
"From Langley Park to Memphis"
The 2014/15 financial results were almost certainly a blip in United’s performance with the difference to the previous season’s impressive results being almost entirely down to the absence from the Champions League.
That has already been addressed this season, so 2015/16 will be the best the club has ever seen in financial terms. As Woodward said, “We are enthusiastic about our strong position, both on and off the pitch. Our record revenue and EBITDA guidance for 2016 reflects the underlying strength of our business and our confidence in its continued growth.”
As statements from senior executives go, that’s about as bullish as it gets. As we have seen over the last couple of years, there’s no doubt that money is available for United to attract star names to Old Trafford, but the onus is now on the team to deliver. Louis van Gaal has been there and done it at many clubs in the past – the question now is whether he can do the same at United.